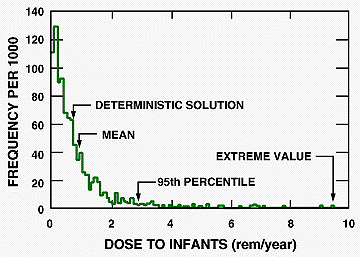


Monte-Carlo-generated frequency distribution of the dose-equivalent to
the thyroid gland of infants (rem/yr) from ingestion of radioiodine-131-contaminated milk.
Values were predicted from an atmospheric dispersion, food chain, and glandular dose model
(Table 1 in reference) with statistical properties of the parameters described in Table 2 (see
reference). Dose calculations are based on a fixed arbitrary release of 1 Ci/yr and constant
wind direction.

How can integrated assessment models be placed into a risk framework?

A regional scale model for atmosphere and foodchain transport of radioiodine was integrated with Monte Carlo simulations to transform the deterministic solution into estimates of risk for higher radiological doses to human infants.

O'Neill, R. V., R. H. Gardner, F. O. Hoffman, and G. Schwarz. 1981. Parameter uncertainty and estimated radiological dose to man from atmospheric 131I releases: A Monte Carlo approach. Health Physics 40:760-764.
Integrated Assessment Briefs. 1995. ORNL/M-4227. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN.